
- All Library Guides
- Research and Resource Guides
- Subject and Course Guides
- Klutznick Law Guides
- Technology Guides
- child* - includes child and children
- disab* - includes disabled, disability, disabilities
- environment* - includes environment, environments, environmental, environmentalist, etc.
- Last Updated: Dec 9, 2025 1:13 PM
- URL: https://culibraries.creighton.edu/health-informatics
- Print Page
Health Informatics
Using Boolean Operators
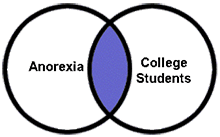 |
The AND operator narrows a search, retrieving only records containing both terms. When building a search, use AND in-between your search concepts/topics. Example: anorexia AND "college students" |
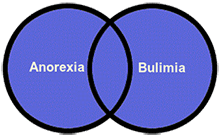 |
The OR operator broadens a search, retrieving records that contain either term, but not necessarily both. It is used to combine synonyms or related concepts. Example: anorexia OR bulimia |
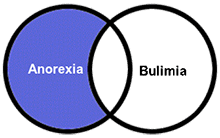 |
The NOT operator narrows a search by removing all records that contain a particular word or phrase. Example: anorexia NOT bulimia Use NOT with caution, as it can screen out useful results. |
Key Search Techniques
Quotation Marks/Phrase Searching
Using quotation marks in a search tells the database that you are looking for an exact phrase. You need to use quotation marks for any phrase that is two or more words. For example, if you were researching Social Security, using quotation marks ["social security"] would tell the database that you only want search results where Social Security appears as a phrase.
Without the quotation marks, the database actually reads your search as [social AND security]. Library databases will interpret strings of terms without any quotation marks or Boolean operators as being connected by the term AND. This is likely to return results unrelated to your research question.
Truncation and Wild Cards
Truncation refers to shortening a word and capturing word variants without having to manually type them all out. Another way of thinking about it is that it tells the database to fill out the rest of the word on its own. In most databases, this is done with an asterisk *.
Examples of truncation:
| Contact: | Creighton University Libraries Creighton University 2500 California Plaza | Omaha, NE 68178-0209 Phone: 402-280-2260 Campus Map |
|---|